
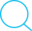
Spring3.2中,已经可以注入包含泛型的List,通过@Autowired注解就可以简单的实现.
@Autowired
private List<Type> beans;
Spring通过GenericCollectionTypeResolver来判断Collection中的泛型类型.
在Spring源码的ListFactoryBean, MapFactoryBean内的createInstance方法中, 都包含GenericCollectionTypeResolver的特殊处理.
GenericCollectionTypeResolver中通过ResolvableType来解析泛型类型.
/**
* Determine the generic element type of the given Collection class
* (if it declares one through a generic superclass or generic interface).
* @param collectionClass the collection class to introspect
* @return the generic type, or {@code null} if none
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public static Class<?> getCollectionType(Class<? extends Collection> collectionClass) {
return ResolvableType.forClass(collectionClass).asCollection().resolveGeneric();
}
/**
* Determine the generic key type of the given Map class
* (if it declares one through a generic superclass or generic interface).
* @param mapClass the map class to introspect
* @return the generic type, or {@code null} if none
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public static Class<?> getMapKeyType(Class<? extends Map> mapClass) {
return ResolvableType.forClass(mapClass).asMap().resolveGeneric(0);
}
/**
* Determine the generic value type of the given Map class
* (if it declares one through a generic superclass or generic interface).
* @param mapClass the map class to introspect
* @return the generic type, or {@code null} if none
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public static Class<?> getMapValueType(Class<? extends Map> mapClass) {
return ResolvableType.forClass(mapClass).asMap().resolveGeneric(1);
}
ResolvableType是Spring 4.0提供的类型解析的API,其中包含丰富简单的泛型操作支持.
ResolvableType的代码是比较优雅的,对于类型的操作都是基于ResolvableType对象本身的.
它提供一系列的for***方法,用于将Class,Field,MethodParamter等类的对象统一转化为ResolvableType对象.
最终通过操作ResolvableType对象来获取类型信息,包括泛型信息(底层通过ParameterizedType来实现).
// Assuming 'field' refers to 's' above
ResolvableType t1 = ResolvableType.forField(field); // List<Custom<Integer>>
ResolvableType t2 = t1.getGeneric(); // Custom<Integer>
ResolvableType t3 = t2.getGeneric(); // Integer
Class<?> c = t3.resolve(); // Integer.class
// or more succinctly
Class<?> c = ResolvableType.forField(field).resolveGeneric(0, 0);
// Assuming 'm' refers to a method that returns MultiValueMap<Integer, String>
ResolvableType t1 = ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(m); // MultiValueMap<Integer, String>
ResolvableType t2 = t1.asMap(); // Map<Integer, List<String>>
ResolvableType t3 = t2.getGeneric(1); // List<String>
ResolvableType t4 = t3.getGeneric(); // String
Class<?> c = t4.resolve(); // String.class
// or more succinctly
Class<?> c = ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(m).asMap().resolveGeneric(1, 0);
值得一提的是,在Spring 4.0中,框架在泛型支持方面,有了极大的提升.
在4.0之前以下行为是不允许的:
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
public Custom<String> stringCustom() {
return new StringCustom();
}
@Bean
public Custom<Integer> integerCustom() {
return new IntegerCustom();
}
}
Spring容器会抛出以下异常:
“No qualifying bean of type [Custom] is defined: expected single matching bean but found 2: stringCustom, integerCustom”
当然,也不是没有办法解决的,你可以通过添加@Qualifier注解,将两个Bean区分开来.
但是在Spring 4.0中,已经可以完全支持此类做法,容器会自动识别泛型类型,在定义与注入中都不会产生异常,甚至可以支持嵌套泛型.
@Autowired
private Custom<String> s1; // Injects the stringCustom bean
@Autowired
private Custom<Integer> s2; // Injects the integerCustom bean
@Autowired
private List<Custom<Integer>> s;