
注:本文为译文,原文出处java-design-patterns-in-stories
策略模式也被称为政策模式.
接下来是一个关于策略模式的故事. 设想迈克有时会超速行使, 但是他不是经常这么干. 他可能会被一个警察拦下来. 可能警察很和善, 会不开罚单让他走也或许只是简单警告一下(让我们将这种警察成为”NicePolice”). 也可能他会被一个严厉的警察拦住并且开了罚单(我们可以称呼这种警察为“HardPolice”). 直到他被拦下来, 他才知道是哪种警察. 这就是策略模式的整个场景.
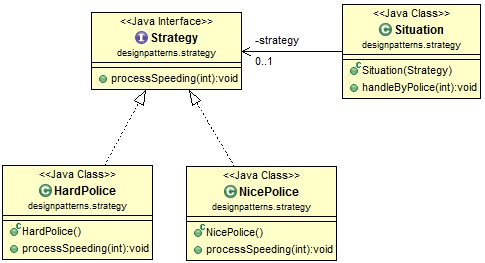
定义一个接口Strategy, 其中包含一个方法processSpeeding()
public interface Strategy {
//defind a method for police to process speeding case.
public void processSpeeding(int speed);
}
现在我们定义两种类型的警察.
public class NicePolice implements Strategy{
@Override
public void processSpeeding(int speed) {
System.out.println("This is your first time, be sure don't do it again!");
}
}
public class HardPolice implements Strategy{
@Override
public void processSpeeding(int speed) {
System.out.println("Your speed is "+ speed+ ", and should get a ticket!");
}
}
定义警察介入处理超速的场景.
public class Situation {
private Strategy strategy;
public Situation(Strategy strategy){
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void handleByPolice(int speed){
this.strategy.processSpeeding(speed);
}
}
最后, 尝试结果.
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]){
HardPolice hp = new HardPolice();
NicePolice ep = new NicePolice();
// In situation 1, a hard officer is met
// In situation 2, a nice officer is met
Situation s1 = new Situation(hp);
Situation s2 = new Situation(ep);
//the result based on the kind of police officer.
s1.handleByPolice(10);
s2.handleByPolice(10);
}
}
输出为:
Your speed is 10, and should get a ticket!
This is your first time, be sure don't do it again!
你可以与状态模式进行比较, 两者非常相似. 主要区别是:状态模式当对象状态发生变化时修改对象的行为, 而策略模式主要是在不同场景应用不同算法.
排序方法在不同场景中使用不同的比较器. 如果想要了解关于此方法的更多内容, 参见Deep Understanding of Arrays.sort.
也可以参考The Difference between Comparator and Comparable.